Prompt Chaining in Generative AI: Break Complex Tasks into Reliable Steps
- Mark Chomiczewski
- 25 December 2025
- 7 Comments
Want your AI to stop making things up? You’re not alone. Every business using generative AI has run into the same problem: the model gives a confident answer that’s completely wrong. A financial report with fake numbers. A customer service reply that misreads a policy. A legal summary that leaves out a critical clause. Single prompts just aren’t enough anymore. That’s where prompt chaining comes in.
What Prompt Chaining Actually Does
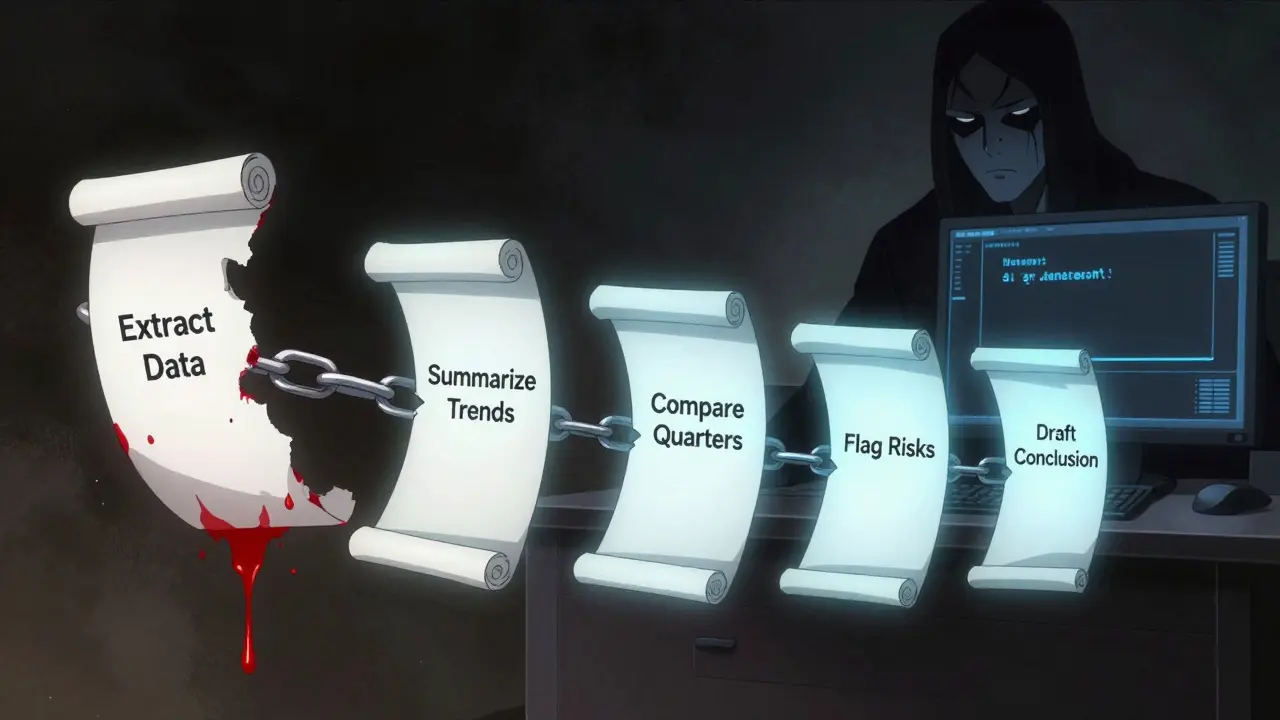
Prompt chaining isn’t fancy jargon. It’s simple: break one big, risky task into smaller, safer steps. Instead of asking an AI to write a market analysis from scratch, you split it up. Step one: gather key data points. Step two: summarize trends. Step three: compare with last quarter. Step four: highlight risks. Step five: draft the conclusion. Each step feeds into the next. The output of step one becomes the input for step two, and so on.This isn’t just about making things slower. It’s about making them accurate. A 2024 IBM study found that using prompt chaining reduced factual errors by 67.3% compared to single-prompt approaches on complex analytical tasks. Why? Because each step can be checked. If step two gets confused, you catch it before it ruins step three. No more cascading lies.
The Five Common Patterns
Not all chains are built the same. Here are the five most reliable patterns used by teams who’ve actually shipped this in production:- Instructional Chaining: Give clear, numbered directions. "First, extract all dates from this document. Then, sort them chronologically. Then, identify the most recent event." Simple. Hard to mess up.
- Iterative Refinement: Start with a rough draft. Then ask the AI to improve it. "This summary is too vague. Add specific metrics. Now make it concise for a CEO." Repeat until it lands.
- Contextual Layering: Don’t dump everything at once. Add context step by step. First prompt: "What’s the company’s revenue?" Second prompt: "Now, compare that to industry averages from 2023." Third: "What does this trend suggest for next quarter?"
- Comparative Analysis: Ask for multiple options, then pick the best. "List three possible interpretations of this customer feedback. Then rank them by likelihood. Then justify your top choice."
- Conditional Branching: Use logic. "If the sentiment is negative, ask for root causes. If it’s positive, identify drivers. If unclear, request clarification."
These aren’t theoretical. Jotform AI users report a 73% improvement in article quality using instructional chaining. Telnyx cut customer ticket escalations by 58% using conditional branching to route issues properly before responding.
Why It Works Better Than Single Prompts
Single prompts are like asking someone to solve a math problem while blindfolded. They might get lucky. Or they might say 2+2=5 and sound totally sure.Prompt chaining is like giving them a calculator, a pen, and paper. They write down each step. You check the math before moving on. Stanford’s April 2024 study showed chaining reduced logical inconsistencies by 31.8% compared to chain-of-thought prompting. Why? Because you control the flow. You force the AI to justify each move.
Forrester’s Q3 2024 report found chaining delivered 4.3x higher accuracy on multi-source reasoning tasks. But there’s a catch: it takes 2.1x longer to design. That’s the trade-off. More upfront work. Way fewer mistakes later.
Where It Falls Short
Prompt chaining isn’t magic. It has limits.First, error propagation. If step one gets something wrong, every step after it inherits that mistake. A Reddit user shared a case where a misconfigured chain caused 100% failure in financial forecasting because the initial data extraction was off by 12%. One bad step. Total collapse.
Second, context drift. After 7 or 8 steps, the AI starts losing track of the original goal. Google’s July 2024 research found chains longer than 8 steps saw accuracy drop by 21%. Keep it tight. Three to five steps is the sweet spot for most tasks.
Third, debugging is hard. If a chain fails, you have to trace through each step. 29% of negative reviews on Capterra mention this as a major pain point. Tools like AWS SageMaker help by logging each prompt and output, but it still takes time.

Who’s Using It - And How
Prompt chaining isn’t just for tech teams. It’s in production across industries:- Financial Services: Banks use it to analyze loan applications. Step one: verify income. Step two: check credit history. Step three: assess risk profile. Step four: recommend approval level. Error rates dropped 61% at one major lender.
- Healthcare: Hospitals chain prompts to summarize patient notes. Step one: extract symptoms. Step two: match to possible conditions. Step three: flag drug interactions. Step four: suggest next steps. Reduces missed diagnoses.
- Legal: Law firms use 7-step chains to review contracts. Each step checks a different clause type. One firm reduced revision cycles by 71% after switching from manual review to chained AI.
- Customer Support: Telnyx automated tier-1 responses using conditional chains. If the query is about billing → pull policy docs. If it’s technical → check KB. If it’s vague → ask for clarification. Escalations dropped 58%.
According to Gartner, 68.3% of Fortune 500 companies now use prompt chaining in at least one workflow. That’s up from 42% in early 2024. Adoption is fastest in tech (31.2%), finance (24.7%), and healthcare (18.3%).
Getting Started - No Experience Needed
You don’t need to be a data scientist to start. Here’s how to begin:- Pick a task that’s currently failing. Something with high stakes - a report, a reply, a decision.
- Break it into 3-5 logical steps. Write them out like a recipe.
- Test each step alone. Make sure the output is clean before chaining.
- Connect them. Use the output of step one as the input for step two. Be precise.
- Add a final check: "Does this answer the original question?"
Promptitude.io’s survey of 1,243 users found most people become proficient in about 29 hours. That’s less than a week of after-work learning. Start small. Try it on drafting email responses. Then move to reports. Then to decision support.
Tools That Help
You don’t have to build this from scratch. These platforms make it easier:- AWS SageMaker: Has built-in prompt chaining tools with logging and human-in-the-loop validation. Launched a new feature on December 1, 2024, that lets you insert a human review point at any step. Beta tests show 83.4% accuracy on legal reasoning tasks.
- Jotform AI: Drag-and-drop chaining interface. Great for non-developers. Used by marketers and HR teams to automate content and forms.
- Promptitude.io: Public library of 1,287 tested chain templates. Filter by use case: legal, marketing, finance.
- LangChain: Open-source framework. More technical, but flexible. Popular with developers building custom AI apps.
Enterprise users give AWS SageMaker 4.7/5 for documentation. Open-source tools average 3.8/5. If you’re new, start with Jotform or Promptitude.io. Save LangChain for later.
The Future: Adaptive Chaining
The next leap isn’t just more steps. It’s smarter steps. Google’s Gemini 2.0, launching in Q2 2025, will have "Auto-Chain" - an AI that automatically designs the best sequence for your task. Microsoft’s Copilot Studio will include chaining by March 2025.Dr. Emily Bowen from Telnyx calls this "adaptive chaining" - where the AI adjusts the chain based on intermediate results. If step two gives a weak answer, the system automatically loops back or adds a clarification step. Early tests show it could cut error rates by another 22-37%.
Right now, only 28% of enterprise chains use AI-assisted design. Gartner predicts that will jump to 65% by 2026. The goal isn’t to replace humans. It’s to make AI reliable enough that humans can focus on what matters: judgment, ethics, creativity.
Final Thought
Prompt chaining isn’t about making AI smarter. It’s about making it honest. It’s about admitting that one big question is too risky. That the best way to get a good answer is to ask smaller, safer questions - and check each one.AI won’t stop hallucinating. But you can stop believing it.
Is prompt chaining the same as chain-of-thought prompting?
No. Chain-of-thought prompting asks the AI to explain its reasoning in one go. Prompt chaining breaks the task into separate, human-designed steps where each output becomes the next input. Chain-of-thought is internal thinking. Prompt chaining is external structure. Stanford’s April 2024 study found chaining had 31.8% fewer logical inconsistencies because it forces clearer boundaries between steps.
How many steps should a prompt chain have?
Most effective chains have 3 to 5 steps. Beyond 7 or 8, accuracy drops due to context drift. Google’s July 2024 research showed error rates increased by 21% after 8 steps. Start simple. If you need more steps, break the task into sub-chains instead of one long chain.
Does prompt chaining slow things down?
Yes, by about 38% on average, according to Promptitude.io’s September 2024 benchmark report. But the trade-off is worth it. A 67% reduction in errors means less time spent fixing mistakes. In customer service, Telnyx found faster resolution times because agents weren’t dealing with wrong answers. Speed matters, but accuracy matters more.
Can I use prompt chaining with free AI tools like ChatGPT?
Absolutely. You don’t need paid tools. Just copy the output of one prompt and paste it into the next. The key is discipline: write each step clearly, test it alone, and keep track of what you’re feeding into the next prompt. Many users on Reddit’s r/AIPromptEngineering do this daily with GPT-4 and Claude 3.
What skills do I need to design good prompt chains?
Three things: logical reasoning (rated essential by 89% of enterprise teams), domain knowledge (76% of users say it’s critical), and understanding AI’s limits (82%). You don’t need to code. But you do need to think like a process designer. If you can break down a task into steps on paper, you can build a prompt chain.
What’s the biggest mistake people make with prompt chaining?
Assuming the AI will fill in the gaps. If step one asks for "relevant data," but doesn’t specify what’s relevant, step two will get garbage. Precision matters. Use exact language. "Extract all dates from the invoice in MM/DD/YYYY format" is better than "Find the dates." Small details prevent big failures.
Is prompt chaining secure for sensitive data?
It depends on the platform. AWS SageMaker and Jotform AI offer private, encrypted processing. Free tools like ChatGPT send data to public servers. For sensitive tasks - medical records, financial data, legal documents - use enterprise platforms with data handling guarantees. The EU AI Act now recommends multi-step validation for high-risk applications, which makes secure chaining a compliance advantage.
Will AI eventually design its own chains?
Yes, and it already is. Google’s Auto-Chain for Gemini 2.0 (Q2 2025) and Microsoft’s Copilot Studio integration (March 2025) will auto-generate chains based on your goal. But even then, you’ll still need to review them. AI can build the structure, but humans still need to define what "good" looks like.
Next Steps
If you’re new to prompt chaining:- Start with a low-risk task: draft meeting notes or summarize a blog post.
- Use a 3-step chain: extract → summarize → refine.
- Track your results. Compare output from single prompts vs. chained prompts.
- Join r/AIPromptEngineering on Reddit. Search for "prompt chain" - there are dozens of real examples.
- Bookmark Promptitude.io’s template library. Use one as a starting point.
If you’re already using it:
- Look for chains longer than 5 steps. Split them.
- Add a validation step after every 2-3 prompts. Ask: "Does this match the original goal?"
- Try AWS’s Human-in-the-Loop feature if you have access.
- Document your chains. You’ll thank yourself when you need to fix one next month.
Prompt chaining isn’t the future. It’s the present. And if you’re still relying on single prompts for anything important, you’re just waiting for the next mistake to happen.



Comments
Eric Etienne
This whole prompt chaining thing feels like overengineering. I just want my AI to spit out a decent email without me writing a fucking instruction manual for it.
December 26, 2025 AT 23:15
Dylan Rodriquez
There's something deeply human about breaking big problems into smaller pieces - it’s how we’ve solved things for centuries. Prompt chaining just gives AI that same structure. It’s not about making AI smarter, it’s about giving it the same patience and discipline we expect from each other. And honestly? That’s kind of beautiful.
When you treat AI like a junior intern who needs clear checklists instead of a psychic, you stop getting weird, confident nonsense. You get reliable results. That’s not magic. That’s just good management.
December 27, 2025 AT 10:11
Amanda Ablan
I started using this for drafting client emails last month. Made a 3-step chain: 1) extract key points from their message, 2) draft a polite response, 3) check tone for over-enthusiasm. Game changer. No more accidentally sounding like a used car salesman.
Also, the Jotform AI interface is so easy. Even my grandma could use it. Seriously.
December 28, 2025 AT 12:14
Meredith Howard
Prompt chaining is essential for high risk applications but the debugging overhead is non trivial
Without proper logging and version control for prompts teams end up with spaghetti chains that no one understands
Enterprise adoption is rising but most teams are not prepared for the operational burden
December 30, 2025 AT 06:18
Yashwanth Gouravajjula
In India we use this for customer service bots. Works. Simple. No drama.
December 31, 2025 AT 14:46
Kevin Hagerty
Wow another blog post pretending AI needs a babysitter. Next they’ll tell us to hold its hand during math class
Just use better models. Stop treating AI like a dumb intern who needs 7 step instructions to make coffee
And btw the 67% error reduction? Probably measured against people asking "write me a report" and expecting Shakespeare
January 1, 2026 AT 11:20
Janiss McCamish
Try this: take your worst-performing task. Break it into 3 steps. Test each one alone. You’ll be shocked how often the problem isn’t the AI - it’s your first prompt.
January 2, 2026 AT 05:48